Periodontitis is a serious gum disease that, if not treated, can damage the soft tissue and lead to the breakdown of the bone supporting your teeth. It is a leading cause of tooth loss in adults. The condition often results from poor oral hygiene, as plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up and hardens on the teeth.
In this article, we’ll explore the most effective treatment options available for periodontitis and help you understand which one might work best for healthier gums.
The Root Cause of Periodontitis
Before discussing treatment, it’s important to understand what causes periodontitis. It all begins with plaque. This sticky substance, made up of bacteria and food particles, can form on your teeth daily. If you don’t remove it by brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which can only be removed by a dental professional.
Tartar leads to inflammation of the gums (gingivitis), the first stage of gum disease. When left untreated, it advances to periodontitis. At this point, the gums start pulling away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. The body’s immune response to this infection starts to break down bone and connective tissue.
Key risk factors include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Certain medications
- Genetic susceptibility
- Hormonal changes in women
Knowing these factors helps in both prevention and treatment planning.
Symptoms to Watch Out For
Periodontitis doesn’t always show clear signs early on. But here are some symptoms that should never be ignored:
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Gums that bleed easily
- Bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth
- Gums pulling away from teeth
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain when chewing
- Changes in the way your teeth fit together
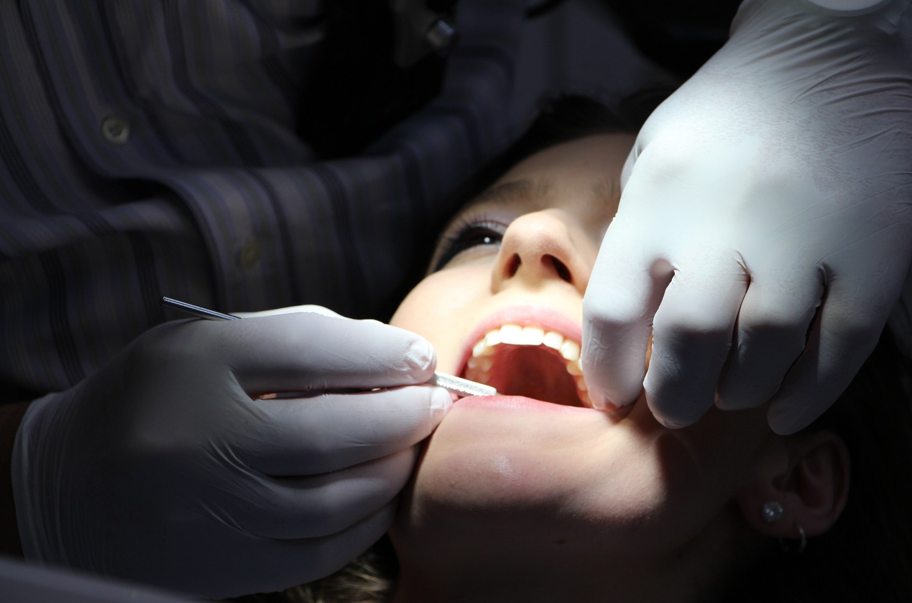
If you notice one or more of these symptoms, it’s time to see a dentist or periodontist for an evaluation.
Non-Surgical Treatments
When diagnosed early, periodontitis can often be treated with non-surgical methods. These aim to remove bacteria and plaque from below the gum line and allow the gums to heal naturally.
Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
The initial approach to managing gum disease typically involves a deep cleaning procedure. During this process, the dentist removes plaque and tartar from both above and below the gum line, a technique known as scaling. This is followed by root planing, which smooths the tooth roots to promote gum healing and encourage reattachment to the teeth.
It may require one or more visits and is usually done under local anesthesia. After the procedure, it’s important to maintain proper oral hygiene to prevent the return of the disease.
Antibiotics
Sometimes, bacteria are stubborn and hard to eliminate with cleaning alone. Dentists may prescribe oral or topical antibiotics. These may be in the form of mouth rinses, gels placed in gum pockets, or tablets.
Antibiotics are typically used in conjunction with scaling and root planing to achieve better results.
Surgical Treatments
In moderate to severe cases of periodontitis, surgery might be needed to restore gum and bone health.
Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery)
In this procedure, the gums are lifted back so tartar can be removed from deep pockets. After cleaning, the gums are stitched back into place to fit snugly around the teeth.
This reduces the pocket depth, making it easier to keep the area clean and preventing future infections.
Bone Grafts
When periodontitis has destroyed the bone around the tooth root, a bone graft can help. This procedure uses small fragments of your bone, synthetic bone, or donated bone to help grow new bone.
Bone grafting is often combined with other regenerative treatments.
Soft Tissue Grafts
If gums have receded, exposing the roots of teeth, a soft tissue graft can cover the roots and reduce further damage. This also improves the appearance of your smile.
Tissue is usually taken from the roof of your mouth and stitched into the affected area.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
This is done along with flap surgery. A mesh-like material is placed between the bone and gum tissue to allow bone and connective tissue to regrow. It helps support teeth better.
Advanced Laser Treatment: A Modern Option
One of the most promising treatments for periodontitis today is LANAP-Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure. This technique uses a special dental laser to target and destroy bacteria without cutting or stitching the gums.
Many patients choose LANAP treatment because it is less painful, promotes quicker healing, and preserves more of the healthy tissue compared to traditional surgery.
Managing Periodontitis with Lifestyle Changes
Treating periodontitis doesn’t end in the dental chair. Your everyday habits play a big role in gum health.
Stop Smoking
Smoking is one of the strongest risk factors for periodontitis. It weakens your immune system, making it harder to fight off gum infections and heal properly after treatment.
Control Diabetes
People with diabetes are more likely to develop infections, including gum disease. Keeping your blood sugar levels under control can help improve treatment outcomes.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Your body needs the right nutrients to fight infections and heal tissues. Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Foods high in Vitamin C, calcium, and antioxidants are especially good for your gums.
Manage Stress
Chronic stress can weaken your immune system and make it harder for your body to fight infection. Simple practices like exercise, meditation, and enough sleep can go a long way in helping your gums heal.
When to See a Periodontist
A general dentist can treat early to moderate gum disease, but for more advanced cases, you may need a periodontist. These are dental specialists who focus on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum disease.
It’s time to seek a periodontist’s help if you have:
- Severe gum recession
- Deep pockets
- Loose teeth
- Bone loss
- Failed past treatments
They can also offer specialized procedures like LANAP and bone regeneration that general dentists may not provide.
Healthier Gums Start with the Right Treatment
Periodontitis is a common but serious dental issue that can be treated and managed with the right care. From deep cleanings and antibiotics to surgical options and advanced laser therapy like LANAP, there are multiple ways to fight this disease.
No matter what treatment you go through, the journey to healthier gums also includes daily brushing, flossing, smart lifestyle choices, and regular dental visits.
Found this article useful? Keep browsing the rest of this section for more.